Warfarin is an active ingredient belonging to the anticoagulant family of drugs. More precisely, it is a vitamin K antagonist that must be administered orally to carry out its therapeutic action. In this article, we will give you a complete guide about the side effects of Warfarin.
Warfarin is found in medicines formulated in tablet form. So, the active ingredient is probably better known by the trade name of the only medicine that currently (September 2020) in our country contains it: Coumadin. However, to be purchased, such medicine would require the presentation of a repeatable medical prescription (RR). However, it is classified as a group A drug. Its cost can be reimbursed by the National Health System (SSN).
What is it for
Warfarin Therapeutic Indications: what is it used for?
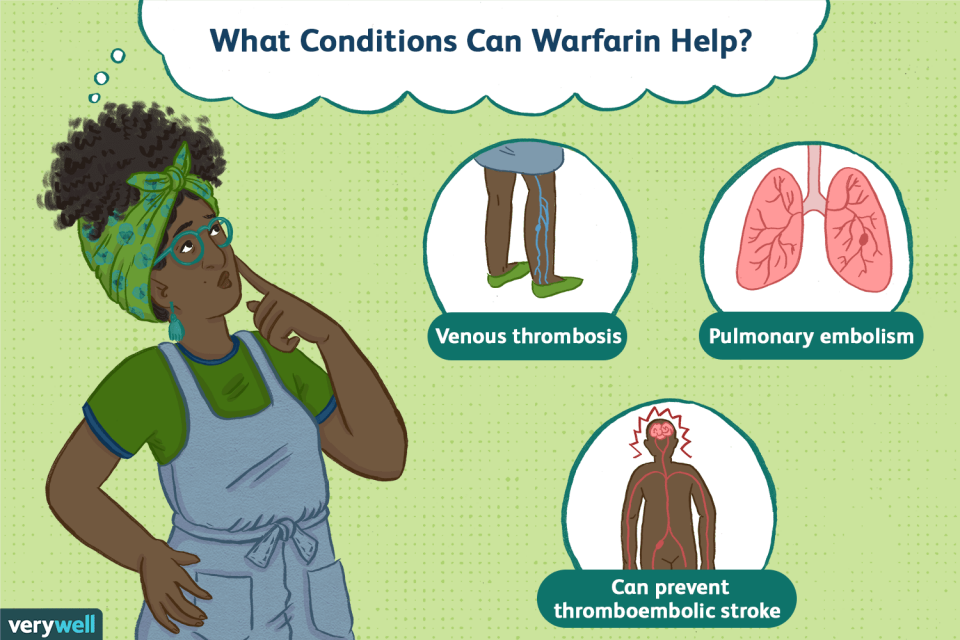
Warfarin is used to prevent the formation of clots in the blood, leading to a blockage of blood flow with all the consequences.
More specifically, Warfarin is used for the treatment and prevention of clots:
- Associated with atrial fibrillation;
- So, Associated with heart valve replacement;
- In the lungs;
- So, In the legs.
However, in patients who have suffered a heart attack, Warfarin is indicated to reduce the risk of a new heart attack, stroke, and decrease the risk of blood clots reaching the legs and lungs.
Side effects of Warfarin: Warnings and Precautions
What you need to know before taking Warfarin orally or parenterally.
Before starting warfarin therapy, it is very important to inform the doctor of any type of disorder or disease. In particular, this health professional must be informed if:
- You notice any signs or symptoms of Bleeding or if you notice any unusual type of Bleeding going on;
- You have suffered from stomach and/or intestinal Bleeding in the past;
- We have or have had in the past an INR above four or very variable;
- You have hypertension or have high blood pressure;
- So, you have anemia, or someone in your family has a blood disorder;
- You have a reduced number of platelets following treatment with heparin (another anticoagulant);
- So, you have an inflammation of the blood vessels;
- There are pathologies involving the blood vessels of the head;
- You have a malignant tumor;
- So, you suffer from kidney and/or liver disorders or diseases;
- You have a catheter;
- So, you must undergo surgery of any kind, including eye and dental surgery;
- You have a pathology involving protein C;
- So, you have diabetes ;
- You have no appetite and eat little;
- They have high levels of blood cells ;
- You have low blood levels of albumin ;
- Hyperphosphatemia or hypercalcemia occurs ;
- You suffer from vitamin K deficiency;
- So, you are taking any medications or foods that contain vitamin K.
During warfarin therapy, on the other hand, the doctor should be immediately warned if:
- The toes turn blue and are sore;
- Vomiting, diarrhea, or infections occur ;
- Necrosis of the skin and tissues appears ;
Interactions
Pharmacological Interactions between Warfarin and Other Drugs
Because of possible drug interactions and the risks associated with them, before starting Warfarin, you should tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken:
- Other anticoagulant drugs;
- Fibrinolytic drugs (used to dissolve blood clots)
- Antibiotic drugs of any type (for example, penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides, sulfonamides, rifamycins, etc.);
- Antifungal drugs ;
- Antiviral drugs ;
- Antiparasitic drugs ;
- Immunosuppressive drugs (for example, cyclosporine, etc.);
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) of any type and corticosteroid drugs ;
- Antidepressant drugs of any type;
- Medicines for the treatment of:
- Insomnia ;
- Epilepsy ;
- Parkinson’s disease ;
- Anxiety and other psychiatric conditions;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland ;
- Urinary incontinence ;
- Symptoms of menopause ;
- Benign prostatic hypertrophy ;
- Cardiac disorders and rhythm disturbances;
- Rheumatoid arthritis ;
- Lack of production of coenzyme Q10 (such as ubiquinone or ubidecarenone);
- Digestive disorders ;
- Gout ;
- Intestinal inflammations.
- Psychostimulants such as methylphenidate;
- Antitussive drugs ;
- Leukotriene antagonists such as zafirlukast;
- Anticancer drugs ;
- Contraceptive drugs ;
- Drugs that increase metabolism ;
- Antidiabetic drugs ;
- Medicines to treat low blood sugar levels
- Antihypertensive drugs;
- Statins, fibrate drugs, and other cholesterol-lowering drugs ;
- Proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists;
- Antiemetic drugs ;
- Danazol ;
- Orlistat ;
- Vaccines ;
- So, Medicines or products (including herbal) for the treatment of dementia;
- Alcohol-containing drugs;
- Ointments containing methyl salicylate or trolamine salicylate;
- So, Hypericum or St. John’s wort drugs and products;
- Medicines and supplements of vitamins E, C, and K.
However, before starting warfarin therapy, you should tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken, or intend to take any kind of drugs or products – even if not expressly listed above – including Medicines without a prescription (SOP), over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, herbal and phytotherapeutic products, etc.
Warfarin with Food and Drinks
During warfarin treatment, it is important not to start diets without first discussing this with your doctor. At the same time, it is necessary to avoid abrupt changes in your eating habits, such as, for example, starting to consume large quantities of foods containing vitamin K (such as, for example, green leafy vegetables such as spinach, lettuce, broccoli, cauliflower, sprouts Brussels and, to a lesser extent, cereals, meat, and dairy products ).
In addition, during warfarin therapy, it is advisable to:
- Avoid alcohol consumption ;
- Avoid taking garlic, Ginkgo biloba, ginseng, echinacea, grapefruit juice, and products that contain them.
However, to know which foods to avoid during treatment with the active ingredient in question, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Side effects of Warfarin
What Unwanted side effects of warfarin Cause?
Warfarin, like any other drug, can cause various side effects Warfarin, although not all patients experience or experience them in the same way. In fact, each person reacts subjectively to the drug’s administration, manifesting undesirable effects different in type and intensity or not showing them at all.
The doctor should be alerted immediately, and treatment stopped immediately if serious side effects appear, such as:
- So, Bleeding and hemorrhages in various parts of the body;
- Skin necrosis or necrosis of other tissues;
- Obstruction of a blood vessel due to fat (systemic atheroemboli and cholesterol microemboli ). So, in these cases, the toes of the foot can become blue and sore ( syndrome blue toe);
- Painful rash (calciphylaxis).
Side effects of Warfarin: Common side effects
- The decrease in hemoglobin, anemia;
- So, Hemorrhage of the eye, rectum, and other parts of the body;
- Hematuria;
- Epistaxis;
Chest and/or belly pain
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting;
- Asthenia, fatigue;
- Swelling from fluid retention;
- Fever;
- Headache;
- dizziness;
- Arthralgia, myalgia;
- Breathing difficulties, hemoptysis;
- Bruising, itching, rash;
- Hypotension;
- Syncope.
Uncommon side effects of Warfarin
- Dyspepsia;
- Dysphagia;
- Flatulence;
- Hematemesis ;
- Hematochezia, melaena ;
- Malaise, chills, pain ;
- Allergic reactions in sensitive individuals;
- Hemothorax ;
- Hemarthrosis;
- Head hemorrhage;
- Vaginal Bleeding;
- Lethargy ;
- Alopecia ;
- Dermatitis , petechiae , urticaria .
Rare side effects of Warfarin
- Bleeding from the back of the abdomen and/or lung
- Hepatitis, jaundice ;
- Anaphylactic allergic reaction ;
- So, total or partial loss of the ability to move;
- Skin necrosis ;
- Vasculitis ;
- So, drop-in blood pressure with a severe reduction in heart function (shock).
Very rare unwanted side effects of Warfarin
- Bleeding around the heart, the liver, and/or adrenal gland;
- Pallor;
- Vertebral hematoma;
- Menorrhagia;
Calcification of the lung
- Bullous dermatitis;
- Blue finger syndrome
- Arterial embolism, embolism fat;
- Necrosis.
- So, Undesirable effects of unknown frequency
- Calciphylaxis;
- Acute kidney damage.
Warfarin overdose
If you have taken too much Warfarin, you should contact your doctor immediately or go to the nearest emergency room.
In the presence of an overdose, the following may occur:
- Abnormal or overt Bleeding (for example, blood in the stool, hematuria, excessive menstrual flow, etc.);
- Small red spots on the skin (petechiae)
- Predisposition to bruising;
- So, Persistent Bleeding from superficial wounds;
- Unexplained reduction in hemoglobin levels.
How does Warfarin work, and with what mechanism of action does it work?
Warfarin carries out its anticoagulant action by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors, namely factors II, VII, IX, and X, and the anticoagulant proteins C and S.
More specifically, Warfarin is thought to do this by inhibiting the regeneration of vitamin K1 epoxide. The degree of depression, however, depends on the dosage administered.
Dosage and method of use
When and How Much Warfarin to Take
As mentioned, Warfarin is available in tablet form for oral use. The tablets should be swallowed whole, either for or close to meals, but at the same time every day.
However, the dosage will be determined by the physician on an individual basis for each patient. So, the dosage may vary over time depending on the patient’s response to the therapy itself.
Moreover, your doctor will determine the right dose based on your prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) values. PT and INR will also be checked periodically during treatment with Warfarin.
Warfarin has a narrow therapeutic index. So, that small variations in the dose taken can have very serious consequences: if excessive, they can cause Bleeding and hemorrhages. If insufficient, they can allow the formation of dangerous blood clots. For this reason, it is essential to carefully follow the instructions provided by the doctor.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Can Warfarin Be Used During Gestation and Breastfeeding?
Because of the damage, it can cause to the unborn child, the use of Warfarin is co- indicated in pregnant women and in women who suspect they are pregnant. The contraindications to using the active ingredient also apply to women of childbearing age who do not use suitable contraceptives.
However, Warfarin is not excreted in breast milk, and infants whose mothers take active substances have not experienced prothrombin time changes. Despite this, the active ingredient should still be used with caution and under medical supervision by breastfeeding mothers. The latter will also need to monitor the child to promptly identify any unexpected bruising or Bleeding.
side effects of Warfarin
Warfarin can cause severe Bleeding, necrosis, or gangrene.
Other possible adverse effects are:
- intestinal gas
- abdominal pain
- swelling
- changes in taste
- hair loss
- cold or chills
So, It is important to contact a doctor right away if taking the drug is associated with:
- urticaria
- rash
- itch
- difficulty in breathing or swallowing
- So, swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, or eyes
- hoarseness
- chest pain or tightness
- So, swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, or calves
- temperature
- infections
- nausea
- He retched
- diarrhea
- excessive fatigue
- lack of energy
- loss of appetite
- So, pain in the upper right side of the stomach
- yellowish discoloration of the skin
- flu-like symptoms
- Contraindications and warnings on the use of Warfarin
- So, Foods and drinks containing vitamin K and smoking can affect how Warfarin works.
Before taking the drug, it is important to inform your doctor:
- of any allergies to the active substance, other substances present in the product, or any other medicinal product;
- if you are already taking warfarin-based medications;
- other medicines, herbal medicines, and supplements taken, remembering to mention in particular: Aciclovir, Allopurinol, Alprazolam, antibiotics, anticoagulants, antifungals, antiaggregants, NSAIDs, Bicalutamide, Bosentan, antiarrhythmics, calcium antagonists, drugs against asthma, anticancer, statins, drugs against HIV, against narcolepsy, against tuberculosis, anticonvulsants, SSRIs, SNRIs, Metoxsalene, Metronidazole, Nefazodone, oral contraceptives, Oxandrolone, Pioglitazone, Propranolol, Vilazodone, Coenzyme Q10, Echinacea, Bilinkoba, Ginkoba, St. John’s wort and Hydrastis Canadensis;
- if you suffer (or have suffered) from diabetes, gastrointestinal infections, wheat allergies;
- So, if you wear a catheter;
- if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- So, It is important to advise surgeons and dentists that you are on Warfarin therapy.
Contraindications
When Warfarin should NOT be used
Warfarin and medicines containing it are contraindicated in all of the following cases:
- Known allergy to Warfarin itself and/or to one or more of the excipients present in the medicine to be taken;
- If you are at risk of bleeding or have ongoing Bleeding;
- So, If you have recently undergone or are currently undergoing surgery – including under local anesthesia – and/or hospital procedures (including back injections);
- If you have very high blood pressure, which can cause malignant hypertension resulting in eye damage;
- During pregnancy, both established and presumed;
- During pregnancy with the risk of miscarriage or with very high blood pressure;
- In women of childbearing age who do not use contraceptive means;
- So, If you are taking any kind of hypericum (St. John’s wort) medicines or products.
PLEASE NOTE
For more information on indications, Warfarin and precautions for use, interactions, method of use and dosage, use in pregnancy and lactation, side effects of Warfarin. So, contraindications of the medicinal product containing Warfarin, ask your doctor for advice and carefully read the package leaflet of the medicine itself.