Prickly heat or miliaria is an ‘ inflammation of the skin caused by obstruction of the sweat glands’ excretory ducts. Prickly heat this obstruction can occur for various reasons, for example, if you sweat too much if the sweat glands are immature (as in the case of infants and young children), if you dress too much if you wear tight clothes if you use certain ointments or skin creams etc. This article will give you a complete guide about how to get rid of heat rash.
Diagnosis is very simple and is based on a quick physical examination and finding the underlying causes.
What are sudamina?
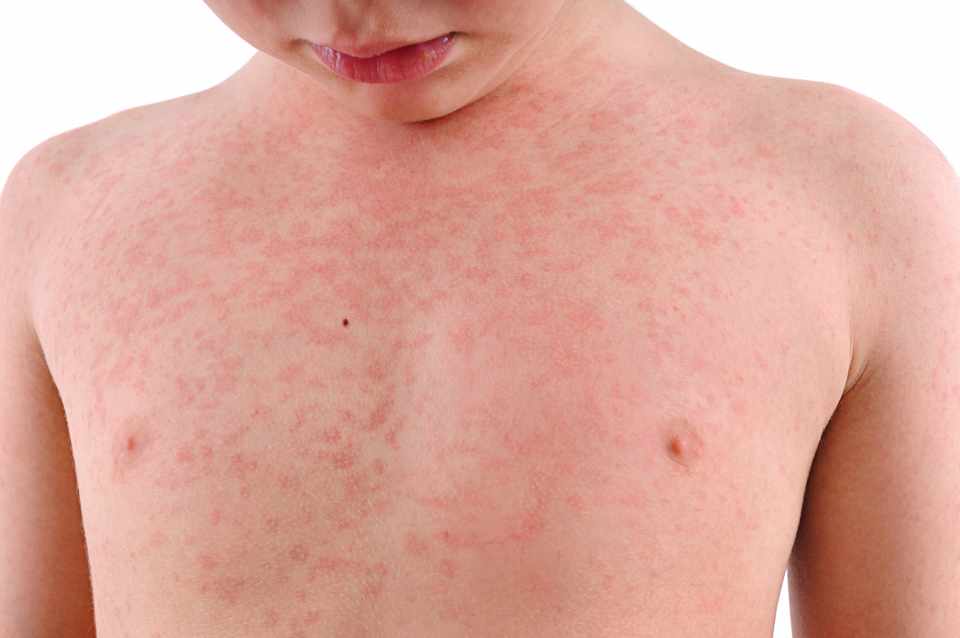
The prickly how to get rid of heat rash, also known as miliaria, is a disorder of the skin’s inflammatory nature, responsible for a rash characterized, depending on the case, by small stains red blistering white, itching or bumps.
Manifestations of sudamina can affect the whole body; however, anatomical areas are more affected than others, such as the neck, shoulders, armpits, chest, back and inner thigh (groin).
The sweat glands are independent structures, composed of their secreting unit (located in a very deep layer of the skin, that is, the hypodermis ) and their excretory duct (through which sweat is expelled). Furthermore, they are richly vascularized and innervated.
Their function is fundamental for the human body because they regulate body temperature, thanks to the emission of sweat. A human being has about 3 million sweat glands scattered everywhere. These glands’ activity is remarkable: just think that, when the temperature rises significantly, they can expel 4-6 litres of sweat in an hour.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Sudamina can affect anyone. However, it is more common among people living in hot-humid climates (for example, tropical areas) and young children.
- Heat rash
- Hives
Urticaria is a rash in the form of small, inflamed blisters. They can affect various parts of the body, form lesions. Depending on the stimuli, several forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Allergic urticaria. May occur as a result of long-term drug treatment.
- Anaphylactoid reaction occurs as a result of the release of accumulated enzymes and proteins from mast cells.
The main reasons for the development of the disease, rash and itching on the body in an adult are:
- liver dysfunction;
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- long-term drug treatment;
- allergic reaction;
- Rash on the skin, accompanied by itching and pain: causes, diagnosis, treatment
- pathology of the digestive system;
- infectious diseases;
- pathology of the endocrine system;
- connective tissue diseases;
- malignant neoplasms.
Scabies
Scabies is caused by exposure of the skin surface to the scabies mite. After infection, the symptoms of a photo may take several hours to show the first signs. The incubation period of the disease is 10-12 days. The scabies rash spreads rapidly throughout the body.
Typical symptoms of infection are:
- severe itching of the affected areas, which intensifies in the evening;
- the appearance of scabies on the surface of the skin;
- the formation of bubbles filled with liquid, erosion, vesicles, crusts;
- the appearance of red, inflamed spots in the abdomen, between the fingers and toes, on the trunk, legs, buttocks, chest, genitals.
During the period of treatment of the rash and from itching on the body in an adult, as well as after undergoing a course of therapy, precautions must be taken. The body does not develop immunity to the disease; after contact with an infected surface, a rash may appear again. With scabies, it is necessary to systematically change bedding, clothes, towels.
When washing, it is necessary to disinfect things, observe personal hygiene rules, and systematically carry out wet cleaning. Therapy consists of medication and external treatment.
Lichen
Lichen is characterized by the formation of nodular rashes on the skin. They are accompanied by severe itching, burning, inflammation.
Depending on the symptoms and causes of occurrence, several types of lichen are distinguished:
- A shingle is a small watery blister that can be accompanied by painful sensations, itching, fever, and inflammation of the lymph nodes. Lichen occurs due to exposure to viral bacteria with reduced immunity, a stressful situation, after an infectious disease.
- The rash on the body of an adult itch flakes.
- Ringworm affects all parts of the body, including the hairy ones. Typical signs are the appearance of red spots, peeling, itching, the appearance of a specific odour, strong brittle hair.
- Lichen planus is characterized by the formation of red bumps with a shiny surface, which forms rings. It occurs on the soles of the feet, legs and can affect the mucous membranes.
- Psoriasis appears as red spots on the folds of the arms, legs, lower back and buttocks. The formations are dry, scaly, can form lesions, are accompanied by itching.
How to get rid of heat rash: Causes
Sudamina occurs when the excretory ducts of the sweat glands become blocked, to the point of preventing sweat from reaching the skin surface and evaporating.
But what are the circumstances that lead to the obstruction of the excretory ducts of the sweat glands?
CIRCUMSTANCES THAT CLOUD THE GLANDS SWEAT
Sweat gland obstruction can be due to:
- Immaturity of the sweat glands themselves. This situation concerns only infants and children, as it is they who have underdeveloped, fragile and easily broken glands; An excessive sweating due to the climatic conditions of the environment. Hot-humid climates promote sweating. Excessive sweating leads to blockage of the excretory ducts and the appearance of the rash typical of sudamina.
- A very intense physical activity. Sport practiced at high levels, particularly heavy work and, in general, and very intense physical activity, cause you to sweat a lot. Excessive sweating, as has been repeatedly mentioned, is a possible cause of sudamina.
- Clothing that is too tight. Tight-fitting clothes prevent adequate elimination of sweat, which can block its flow path by stagnating in the excretory ducts. It is no coincidence that those who habitually wear tight-fitting clothes are more subject to miliaria.
- Certain drugs. Some medicines, such as clonidine, beta-blockers and opiates, increase the activity of the sweat glands and increase the production of sweat.
- Occlusive skin ointments and creams. Applying certain skin products can block the excretory ducts and prevent sweat from escaping. Sudamina, in these cases, also occurs when sweating is normal.
- Exaggerated clothing. Over-dressing or over-covering at night can cause you to sweat a lot and consequently cause a blockage of the excretory ducts.
RISK FACTORS
The individuals most easily subject to sweat are those who: live in areas with a hot-humid climate, such as the tropics; engage in activities (no matter whether sports or work) that make you sweat a lot; are overweight or obese; they have a habit of wearing more clothes than necessary; To these risk, categories are added infants and children because they still have immature sweat glands, more prone to obstruction.
How to get rid of heat rash: Symptoms
For further information: Miliaria Symptoms, The most characteristic sign of sudamina is a rash (also called a rash or exanthema ) characterized by the appearance of:
- papules (small red spots )
- blisters
- They are sometimes itching.
Clothes promote sweating and reduce the evaporation of sweat produced by the glands.
Depending on the layer of skin where the excretory duct of the sweat gland is blocked, sudamina can be divided into crystalline sudamina (or miliaria crystalline), sudamina Rubra (or miliaria rubra) and deep sudamina (or deep miliaria).
CRYSTALLINE SUDAMINE
So, Crystalline prickly heat or crystalline miliaria, prickly heat is the form of more moderate and less severe: in most cases, it tends to resolve spontaneously within a few days. Crystalline sudamina are the most common form among infants. However, it can also affect adults.
SUDAMINA RUBRA
The prickly heat Rubra, or miliaria rubra, arises when the excretory ducts are blocked at the level of the deeper layers of the epidermis.
- Small bumps of red colour
- Itching and stinging pain, similar to the prick of a thorn, in the affected regions
- Reduced or completely absent sweating ( anhidrosis ) in the affected regions
Sudamina Rubra affects adults more than children and represents the typical form of tropical climates and bedridden conditions due to a serious illness.
On some rare occasions, it can give rise to pimples; in this case, we also speak of pustular sudamina or pustular miliaria.
DEEP SUDAMINA
The deep sudamina, or deep miliaria, in the form of more severe prickly heat, but, at the same time, it is also the least common. Typical of adults, it usually arises after repeated episodes of sudamina rubra or as a complication of the latter. The excretory duct’s obstruction occurs in the dermis, which is one of the deepest layers of the skin.
The skin rash may involve non-itchy, flesh-coloured bumps or a reaction very similar to goosebumps. The anatomical regions involved do not emit sweat (anhidrosis), so much so that the patient may be the victim of heatstroke, with dizziness, nausea and rapid heartbeat.
WHEN TO SEE THE DOCTOR?
Most cases of sudamina resolve spontaneously, within a few days and without special treatments. However, if your symptoms do not show any improvement or if the affected areas unexpectedly become swollen, painful and purulent, it is advisable to contact your doctor and request an appointment, as it could be an infection.
Signs of an ongoing infection, which should attract the patient’s attention:
- Worsening of pain, swelling and redness in the area affected by the rash
- Sense how to get rid of heat rash at the exanthematic area (i.e. the area with the rash)
- Release of pus from papules or blisters
- Swollen lymph nodes in the armpits, neck or groin (when, of course, the rash has appeared in these anatomical regions)
- Fever or chills
How to get rid of heat rash: COMPLICATIONS
In addition to bacterial infections, sudamina can also lead to another dangerous complication: getting rid of heat rash. This, as anticipated, is typical of cases of deep miliaria (therefore, it is rare), that is, situations in which there is a deep obstruction, at the level of the dermis, of the excretory ducts.
Symptoms of heatstroke are drop in blood pressure ( hypotension ), dizziness, nausea, headache, and a rapid heartbeat. The people most prone to sweat-induced heatstroke are individuals who live in very hot geographic areas.
SUDAMINE IN CHILDREN
In infants and children, the characteristic rash is most common on the neck, shoulders, and chest, while it is less common on the armpits, elbows, and groin regions.
Diagnosis
In fact, an objective examination is sufficient, during which the doctor observes the skin rash and tries to discover its causes.
TRACKING THE CAUSES
To understand what caused the sudamina, the doctor asks the patient (or family members, if the patient was a newborn or small child) the type of work performed, the sporting activity practiced. The type of clothing usually worn. So, The drugs are taken, the environment in which he usually lives, if there was a particular event that triggered the symptoms, etc.
How to get rid of heat rash: Treatment
Sudamina, especially when it is mild, tends to resolve spontaneously within a few days.
DO NOT SWEAT!
When you suffer from sweat, to heal faster, simply avoid sweating too much for a few days. To succeed in this attempt, it is a good idea:
- Avoid dressing too much unless the temperature of the external environment makes it essential.
- Avoid dressing incorrectly when exercising.
- Improve the work or home environment by ventilating the area where you spend most of your time. This solution is particularly suitable for patients who periodically suffer from sudamina.
- Don’t cover yourself up too much at night.
LOCAL ADMINISTRATION DRUGS
The most serious rashes and at risk of complications are treated with locally administered drugs (NB: local administration means that the drug is applied directly to the exanthematous area).
Anhydrous lanolin, prevent blockage of the excretory ducts and improve skin rashes scattered throughout the body, and corticosteroids, for papules and more severe pustules.
Beware of corticosteroids
They can cause serious side effects such as high blood pressure, increased body weight, osteoporosis, glaucoma, diabetes, and muscle weakness.
OTHER USEFUL TIPS
Clothes that are too tight and some preparations to spread on the skin slow down the sudamina’s healing, if not cause it to deteriorate. Therefore, it is a good idea to wear loose clothing, breathe the skin, and avoid unnecessary skin creams or lotions.
How to get rid of heat rash: Prevention
To protect yourself from the onset of sudamina, the following precautions may be enough:
- In summer, wear light, loose-fitting, cotton clothing; in winter, cover up appropriately for the temperature.
- Avoid all tight-fitting clothes made of skin-irritating material.
- If the weather is hot, equip the room where you spend most of the day with an air conditioner or ventilation system.
- Don’t over-cover yourself at night.
- Do not spread skin creams and ointments unless necessary. Avoid occlusive products.