The female body is enigmatic. It is a labyrinth of biological processes and hormonal activities. Women have to deal with menstruation, pregnancy, oily skin, and that is only a handful. Late teens and early ’20s are critical for women as often signs of irregular periods, acne, or weight issues become prevalent. As the symptoms pile up, the medical diagnosis may conclude you have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, or commonly known as PCOS. Know what are the signs of PCOS in order to contain it immediately.
What do ovaries do?
Before understanding the symptoms and diagnosis of PCOS, it is essential to note how ovaries work and contribute. Ovaries are vital to the female reproductive system as they are responsible for ovulation, releasing an egg during each menstrual cycle. They are small and oval-shaped organs present close to the pelvic region. The matured egg is pushed down the fallopian tube from the ovary to enable fertilization.
Features of PCOS
Signs of PCOS is rather common among women across the world. Cases have been reported to be asymptomatic, where women are diagnosed with PCOS but do not display any symptoms.
The key features attributed to PCOS are –
- Irregular periods: It is caused due to irregular or failed ovulation by the ovaries
- Increased levels of insulin or androgen: Insulin is a pancreatic hormone, while androgen is dominantly a male hormone. High levels of the two can attribute to physical changes like hirsutism or acne.
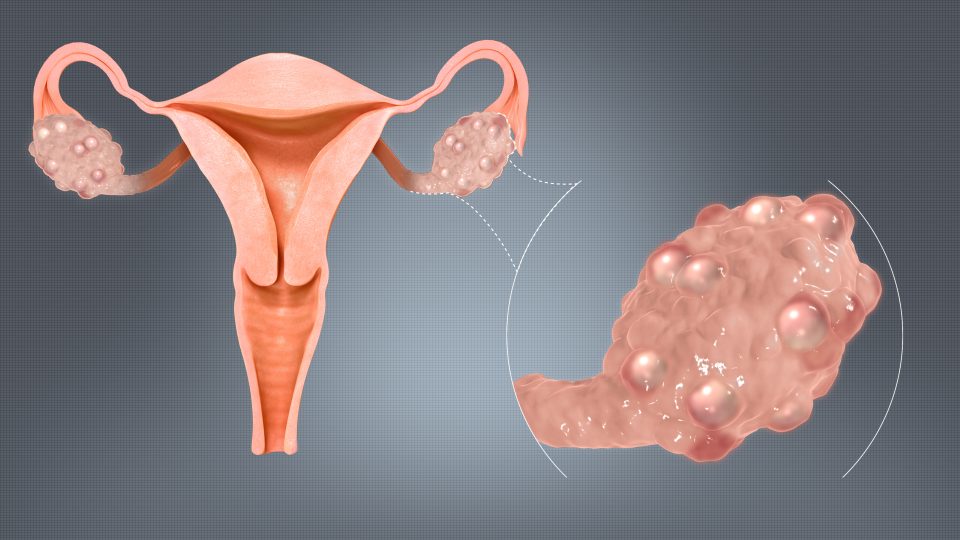
- Polycystic ovaries: Results in enlarged ovaries and fluid-filled follicles that surround the eggs and adversely affect ovulation. As a result, women with PCOS have problems getting pregnant.
The science behind Polycystic Ovaries
PCOS affects how women’s ovaries function. However, the signs of PCOS are not confined to just the ovaries. Also, women do not develop “cysts” in their ovaries, as the name may suggest.
Polycystic ovaries contain numerous harmless follicles, sized about 8mm. Now follicles are little sacs where the egg (or, ova) develops. In the case of PCOS, these are unable to release eggs, so ovulation does not occur. The absence or irregular release of eggs results in irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances.
Causes of signs of PCOS
Medical science still cannot determine the precise cause or origin of PCOS in women. Generally, symptoms arise for women in their late teens and early ‘20s. The roots of PCOS can be traced to an array of factors that may or may not be determinant –
Heredity
The family medical history containing signs of PCOS cases or type 2 diabetes can pass on the problems to future generations. However, it is not characteristic of a single gene to cause PCOS. It is a highly complex relation in heredity and genetics that involves multiple genes.
High levels of androgen
Androgen is known as the “male hormone.” However, it can be detected in both male and female bodies in varying proportions. Body tissues in women produce smaller traces of the hormone, as well as in ovaries and adrenal glands. Raised levels of androgen in women can arise excessive body and facial hair growth, oily skin, and acne, ultimately resulting in PCOS.
Insulin resistance
Insulin is another hormone in the body released by the pancreas in men and women alike. Higher levels of insulin compel the body cells to become resistant to the hormone. The entry of glucose into the cells is blocked as a result. As the insulin levels soar in the body, the androgen production also increases, and ovulation becomes difficult.
Lifestyle and diet
PCOS is exclusive to any particular body type or weight. However, weight and dietary habits play a role in determining the causes of PCOS. Obese women with improper diet and lack of physical activity have higher chances of insulin resistance and, subsequently, PCOS.
Inflammation
Women with PCOS can also have a low-grade inflammation that stimulates androgen production in the ovaries.
Symptoms and Signs of PCOS
PCOS includes several symptoms, and their presence varies among individual women. While some cases are mild, and only a couple of symptoms are prevalent, for other cases, women may show severe symptoms. Symptoms also differ based on the stage of life, lifestyle, and diet of various women.
Here are some common symptoms related to PCOS in women –
Periods
The irregularities in hormones, namely androgen and insulin, disrupt normal menstruation of women. As a result, ovulation does not follow the monthly cycle. PCOS may be the reason behind irregular periods. The regular cycle of menstruation is considered to be 28 days. However, anywhere between 21 to 35 days may also happen. With a delay in menstruation, ovulation can potentially stop entirely or occur only occasionally. Women with PCOS also tend to bleed severely or lightly during periods. Younger girls diagnosed with PCOS can have their periods starting late as well.
Reduced fertility
Women with PCOS should not be deemed as infertile. Irrespective of whether someone is diagnosed with PCOS, they can bear children. However, due to irregular periods and failed ovulation, a natural pregnancy may be difficult. Women with PCOS may require medical assistance or some form of fertility treatments to conceive children. They also face higher possibilities of pregnancy complications.
Excess hair
Commonly known as “hirsutism,” PCOS can cause excessive body and facial hair growth on women. PCOS commonly results in higher levels of androgen, which is predominant in males. Androgen stimulates the hair follicles that grow thick and darker hair. The excess growth can be observed in areas where men have more hair, such as sideburns, chin, upper lip, chest, lower abdomen, and thighs. Though the hair growth problem is not necessarily characteristic of PCOS, it is related to ethnicity. South Asian women like Indians and Sri Lankans usually have thicker body hair, and PCOS can aggravate its growth.
Hair loss
On the contrary, higher levels of androgen can also result in hair loss or alopecia. It can be observed by a receding front hairline or thinning of the top of the scalp. The symptoms can vary according to the stages of the lives of women and their lifestyles.
Skin Conditions
PCOS usually increases the oil production of glands in the skin and cause acne. Now, acne is prevalent in adolescents. Nevertheless, young women with PCOS tend to have more severe cases. Skin tags, which have thickened lumps of skin and rough, dark patches of skin, also show on armpits and necks of women with PCOS.
Psychological effects
The domain of mental health and its association with PCOS and hormonal disbalances is still under extensive research. The bodily changes and coping with conditions like hirsutism, acne, weight changes, and fertility problems influence women’s mental well-being. It may lead to depression, anxiety, body image issues, and bring down self-esteem and feminity. Late diagnosis of PCOS can also deter mental health. The symptoms start showing, and weight management, hair growth, skin conditions can tend to be depressing. Being unaware of the medical condition may affect lifestyle and put you through a negative cycle.
As it is evident, the symptoms of PCOS are multiple, and there is no one-track diagnosis. The symptoms can be summarised based on how they are affecting different parts of a woman’s body:
Periods and Fertility
- No periods or irregular periods
- Immature ova that do not mature
- Difficulties in natural pregnancy
- Pregnancy-related complications
Hair, skin, and body
- Excessive hair growth on body or face (hirsutism)
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Darkened skin patches (acanthosis nigricans)
- Increase in weight
Mental Health
- Mood changes
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Low self-respect
- Undermining body image
- Impact on lifestyle
PCOS related health conditions
Since PCOS is affecting hormonal activities and bringing physical changes to women, it ultimately results in more long-term health effects –
Infertility
Though diagnosis with PCOS does not mean infertility for the women, it does affect ovulation and may result in a complete stoppage of egg release and maturity. It causes hormonal imbalances and is one of the leading causes of infertility in women.
Weight gain and related problems
Weight management becomes hard for women with PCOS. As a result, weight gain increases the chances of diabetes, high blood pressure, and issues with cholesterol. Severe cases may result in heart-related problems and strokes.
Sleep Apnea
It is a specific condition where women have pauses in breathing while sleeping. It is more noticeable in obese women with PCOS and causes trouble in sleeping.
Endometrial Cancer
During ovulation, the lining of the uterus sheds. PCOS affects the regular ovulation cycle, and as a result, the uterine lining thickens over time. The build-up may increase the chances of endometrial cancer.
Depression and other mental health issues
PCOS directly causes hormonal imbalances and fertility problems in women. The symptoms give rise to mood swings, body image issues, undermines sexuality, and feminity. Women with PCOS need assistance in coping with the changes and signs, which may otherwise lead to depression and anxiety.
- Inflammation of the liver due to accumulation of fat (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis)
- Gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure
- Miscarriage or premature birth arising from complications during pregnancy
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of PCOS is inferred based on a minimum of two out of three significant symptoms –
- Irregular periods
- High levels of androgen
- Presence of multiple cysts in the ovary
Abnormal hair growth, acne, weight issues follow the primary diagnosis. Doctors conduct some tests to analyze the problems associated with the ovaries and other parts of the reproductive tract. The Pelvic Test is a direct approach where the examiner inserts a gloved hand into the vagina and investigates for growths or protrusions in the ovaries and uterus. Blood tests are conducted to determine the levels of hormonal activities in the body, along with assessments of the cholesterol and insulin levels. Ultrasounds report can also help visualize any abnormalities in the ovaries and uterus.
The evaluation conducted is aimed to detect PCOS in the body and predict the possible risks of heart problems and diabetes.
PCOS treatment
PCOS can be treated by regularizing the menstrual cycle and controlling other symptoms through birth control pills and other medication. Inducing a prescribed daily dose of estrogen and progestin contributes to restoring healthy hormonal balance, regulate ovulation, and control excessive hair growth, acne, oily skin, etc. They also mitigate the possibility of developing endometrial cancer.
Metformin is a type of drug used to treat type 2 diabetes by improving insulin levels to normalcy. The drug is effective in weight control, managing blood sugar levels, and maintaining a periodic menstrual cycle when aided by a healthy, balanced diet and substantial physical exercise. Clomiphene is a fertility drug that helps with pregnancy in cases of PCOS.
Unwanted hair can be removed through hair removal procedures like laser or electrolysis. Eflornithine cream is a prescription drug that helps slow down the growth of hair.
Surgery is always an available option when it comes to improving fertility. Medical procedures like Ovarian Drilling uses lasers or thin heated needles to make tiny holes in the ovary, which can help normalize ovulation and counter the effects of PCOS.
Indicators of PCOS
So now the question arises, when should you visit a doctor? There are some interpretive signs you should observe that indicate you may require medical advice and have a possibility of developing PCOS –
- When you have missed your periods, and you are not pregnant
- If you find excess and unwanted hair growth on the face and body
- When your symptoms are comparable to diabetes, like sudden weight loss, blurred vision, excess thirst or hunger
- If you are trying to get pregnant for over 12 months to no effect
When you start showing multiple symptoms of PCOS, consult a doctor immediately. Gynecologists and endocrinologists can support you with specialized advice and thoroughly conduct assessments. Keep up with medical check-ups if you are diagnosed with PCOS. Regular blood sugar tests, blood pressure tests should be imperative.
Signs of PCOS is also primarily controlled by maintaining an active lifestyle and a healthy diet. Weight loss and proper management can help mitigate the risks and even help in recovery. Exercise and diet also help with fertility and improving the odds of getting pregnant. Hence, lead a healthy lifestyle and diagnose for PCOS as soon as you develop symptoms. Early diagnosis can go a long way in damage control. It is always important to stay safe and informed.